springfox 源码分析(一) 程序入口
日期:2019-5-21 21:05:15
地点:家中
前言
最近也是闲来无事,加上对swagger-bootstrap-ui也已经发布了将近26个稳定版本了,想到很多以后更有趣的功能,从Java底层扩展插件的方式开发出让国人拥有更棒的文档体验,所以决定研究一下springfox的源码,看能否对自己有一些启发.开发一些有趣的功能呢.
关于springfox的使用这里不做过多的说明,可以自行搜索查看帮助文档,或者可以参考我提供的swagger-bootstrap-ui-demo进行swagger的集成示例.
在读springfox的源码之前,我们需要知道他具体的作用是什么?
我觉得有以下几点:
- 对Spring的RestController、Controller接口进行包装,封装输出为Swagger规范中的path
- 针对Rest接口涉及到的model进行解析,包括model的属性等
- 满足文档分组的要求,解析tags
总结一句话就是:输出符合Swagger API规范的JSON格式
Swagger 规范
OpenAPI 2.0 规范可以参考官网地址:https://swagger.io/specification/v2/
先来看我们的Swagger规范文件包含哪些元素
{
"swagger": "2.0",
"info": {
"description": "<div style='font-size:14px;color:red;'>swagger-bootstrap-ui-demo RESTful APIs</div>",
"version": "1.0",
"title": "swagger-bootstrap-ui很棒~~~!!!",
"termsOfService": "http://www.group.com/",
"contact": {
"name": "group@qq.com"
}
},
"host": "127.0.0.1:8999",
"basePath": "/",
"tags": [
{
"name": "1.8.2版本",
"description": "Api 182 Controller"
}
],
"paths": {
"/2/api/new187/postRequest": {
"post": {
"tags": [
"api-1871-controller"
],
"summary": "版本2-post请求参数Hidden属性是否生效",
"operationId": "postRequestUsingPOST_1",
"consumes": [
"application/json"
],
"produces": [
"*/*"
],
"parameters": [
{
"in": "body",
"name": "model187",
"description": "model187",
"required": true,
"schema": {
"originalRef": "Model187",
"$ref": "#/definitions/Model187"
}
}
],
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "OK",
"schema": {
"originalRef": "Rest«Model187»",
"$ref": "#/definitions/Rest«Model187»"
}
},
"201": {
"description": "Created"
},
"401": {
"description": "Unauthorized"
},
"403": {
"description": "Forbidden"
},
"404": {
"description": "Not Found"
}
},
"security": [
{
"BearerToken": [
"global"
]
},
{
"BearerToken1": [
"global"
]
}
],
"deprecated": false
}
}
},
"securityDefinitions": {
"BearerToken": {
"type": "apiKey",
"name": "Authorization",
"in": "header"
}
},
"definitions": {
"AInfoVo": {
"type": "object",
"required": [
"aId",
"bList"
],
"properties": {
"aId": {
"type": "string",
"description": "A记录主键"
},
"bList": {
"type": "object",
"description": "B信息Map, key为BInfoVo的主键pkId",
"additionalProperties": {
"originalRef": "BInfoVo",
"$ref": "#/definitions/BInfoVo"
}
}
},
"title": "AInfoVo",
"description": "A信息"
},
"ActInteger": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"doub1": {
"type": "number",
"format": "double",
"description": "double类型属性"
},
"float1": {
"type": "number",
"format": "float",
"description": "float类型属性"
},
"name": {
"type": "string"
},
"number": {
"type": "integer",
"format": "int64",
"description": "Long类型"
},
"price": {
"type": "number",
"description": "BigDecimal类型属性"
},
"sort": {
"type": "integer",
"format": "int32",
"description": "int类型"
}
},
"title": "ActInteger"
},
"Actor": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"address": {
"type": "string"
},
"deepOne": {
"originalRef": "DeepOne",
"$ref": "#/definitions/DeepOne"
},
"recipt": {
"originalRef": "Recipt",
"$ref": "#/definitions/Recipt"
},
"sort": {
"type": "integer",
"format": "int32"
}
},
"title": "Actor"
}
}
}
一个标准的Swagger接口规范可能类似上面的JSON文件,主要有以下属性:
- swagger:当前swagger的版本号
- info:文档的基础信息,包括描述信息,标题、作者、host等
- tags:分组tag标志
- paths:接口明细集合
- securityDefinitions:权限信息
- definitions:接口涉及到的Model类型定义
使用
我们对Swagger的规范定义有了一个初步的了解,所以,接下来,我们来查看springfox是如何来实现的
我们在使用springfox-swagger的时候主要有两步:
- 创建
Docket实例对象,并使用@Bean注解注入到Spring容器中 - 在Swagger的配置类上添加
@EnableSwagger2注解
开始
我们从springfox的使用文档上来看,也仅仅知道告诉我们开发人员,需要从@EnableSwagger2这个注解入手,来跟踪springfox的创建流程
但是我在看了该注解后,发现其实并不是这样,springfox源码中使用了大量的Spring的@Component注解进行实体bean的注入,所以要想找到各个类的依赖关系可以说是相当复杂,加上使用了Spring项目中并不怎么流行的spring-plugin组件,这更加增加了的阅读源码的难度,说实话,看过之后,已经留下了眼泪(这乱七八糟的什么玩意儿:( ).....
@EnableSwagger2
先来看EnableSwagger2注解的代码
package springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.configuration.Swagger2DocumentationConfiguration;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* 配合Java配置注解@Configuration使用,启用Swagger的配置注解,使用@Import注解导入Swagger文档的Configuration配置初始化类
* @see springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket
*/
@Retention(value = java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(value = { java.lang.annotation.ElementType.TYPE })
@Documented
@Import({Swagger2DocumentationConfiguration.class})
public @interface EnableSwagger2 {
}
@EnableSwagger2注解只干一件事,导入Swagger2DocumentationConfiguration配置类
Swagger2DocumentationConfiguration
继续看Swagger2DocumentationConfiguration的代码
@Configuration
@Import({ SpringfoxWebMvcConfiguration.class, SwaggerCommonConfiguration.class })
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {
"springfox.documentation.swagger2.mappers"
})
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
public class Swagger2DocumentationConfiguration {
@Bean
public JacksonModuleRegistrar swagger2Module() {
return new Swagger2JacksonModule();
}
@Bean
public HandlerMapping swagger2ControllerMapping(
Environment environment,
DocumentationCache documentationCache,
ServiceModelToSwagger2Mapper mapper,
JsonSerializer jsonSerializer) {
return new PropertySourcedRequestMappingHandlerMapping(
environment,
new Swagger2Controller(environment, documentationCache, mapper, jsonSerializer));
}
}
从代码中,我们可以得知:
- 注入
JacksonModuleRegistrar实体bean到Spring容器中 - 注入一个
HandlerMapping实体Bean到Spring容器中,该接口就是我们经常所见的/v2/api-docs接口 - 扫描
springfox.documentation.swagger2.mappers包路径,进行实体bean的注入工作 - 导入
SpringfoxWebMvcConfiguration和SwaggerCommonConfiguration配置类
既然知道了swagger提供接口代码所在,那么我就先来看看Swagger2Controller的风采
@Controller
@ApiIgnore
public class Swagger2Controller {
public static final String DEFAULT_URL = "/v2/api-docs";
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Swagger2Controller.class);
private static final String HAL_MEDIA_TYPE = "application/hal+json";
private final String hostNameOverride;
private final DocumentationCache documentationCache;
private final ServiceModelToSwagger2Mapper mapper;
private final JsonSerializer jsonSerializer;
@Autowired
public Swagger2Controller(
Environment environment,
DocumentationCache documentationCache,
ServiceModelToSwagger2Mapper mapper,
JsonSerializer jsonSerializer) {
this.hostNameOverride =
environment.getProperty(
"springfox.documentation.swagger.v2.host",
"DEFAULT");
this.documentationCache = documentationCache;
this.mapper = mapper;
this.jsonSerializer = jsonSerializer;
}
@RequestMapping(
value = DEFAULT_URL,
method = RequestMethod.GET,
produces = { APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE, HAL_MEDIA_TYPE })
@PropertySourcedMapping(
value = "${springfox.documentation.swagger.v2.path}",
propertyKey = "springfox.documentation.swagger.v2.path")
@ResponseBody
public ResponseEntity<Json> getDocumentation(
@RequestParam(value = "group", required = false) String swaggerGroup,
HttpServletRequest servletRequest) {
String groupName = Optional.fromNullable(swaggerGroup).or(Docket.DEFAULT_GROUP_NAME);
Documentation documentation = documentationCache.documentationByGroup(groupName);
if (documentation == null) {
LOGGER.warn("Unable to find specification for group {}", groupName);
return new ResponseEntity<Json>(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
Swagger swagger = mapper.mapDocumentation(documentation);
UriComponents uriComponents = componentsFrom(servletRequest, swagger.getBasePath());
swagger.basePath(Strings.isNullOrEmpty(uriComponents.getPath()) ? "/" : uriComponents.getPath());
if (isNullOrEmpty(swagger.getHost())) {
swagger.host(hostName(uriComponents));
}
return new ResponseEntity<Json>(jsonSerializer.toJson(swagger), HttpStatus.OK);
}
private String hostName(UriComponents uriComponents) {
if ("DEFAULT".equals(hostNameOverride)) {
String host = uriComponents.getHost();
int port = uriComponents.getPort();
if (port > -1) {
return String.format("%s:%d", host, port);
}
return host;
}
return hostNameOverride;
}
从接口代码中,我们得知:
- springfox为我们提供了一个默认的接口
/v2/api-docs - 同时我们也应该知道,springfox的初始化工作不在这里,springfox在应用启动时已经初始化好相应的文档对象
Documentation,而接口此处仅仅只是从缓存对象中获取而已
SpringfoxWebMvcConfiguration
通过名称,我们可能也猜到了一部分内容,这是和Spring的webmvc相关的配置类,来看具体代码:
@Configuration
@Import({ ModelsConfiguration.class })
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {
"springfox.documentation.spring.web.scanners",
"springfox.documentation.spring.web.readers.operation",
"springfox.documentation.spring.web.readers.parameter",
"springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins",
"springfox.documentation.spring.web.paths"
})
@EnablePluginRegistries({ DocumentationPlugin.class,
ApiListingBuilderPlugin.class,
OperationBuilderPlugin.class,
ParameterBuilderPlugin.class,
ExpandedParameterBuilderPlugin.class,
ResourceGroupingStrategy.class,
OperationModelsProviderPlugin.class,
DefaultsProviderPlugin.class,
PathDecorator.class,
ApiListingScannerPlugin.class
})
public class SpringfoxWebMvcConfiguration {
@Bean
public Defaults defaults() {
return new Defaults();
}
@Bean
public DocumentationCache resourceGroupCache() {
return new DocumentationCache();
}
@Bean
public static ObjectMapperConfigurer objectMapperConfigurer() {
return new ObjectMapperConfigurer();
}
@Bean
public JsonSerializer jsonSerializer(List<JacksonModuleRegistrar> moduleRegistrars) {
return new JsonSerializer(moduleRegistrars);
}
@Bean
public DescriptionResolver descriptionResolver(Environment environment) {
return new DescriptionResolver(environment);
}
@Bean
public HandlerMethodResolver methodResolver(TypeResolver resolver) {
return new HandlerMethodResolver(resolver);
}
}
从代码中能知道:
- 注入了文档缓存DocumentationCache实体bean
- 注入了JSON序列化实体bean
- 通过
EnablePluginRegistries注解,开启Spring-Plugin组件的相关插件类,关于Spring-Plugin我们后面会说明 - 扫描相关package路径
- 导入
ModelsConfiguration配置文件
来看ModelsConfiguration配置类有做了那些操作呢
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {
"springfox.documentation.schema"
})
@EnablePluginRegistries({
ModelBuilderPlugin.class,
ModelPropertyBuilderPlugin.class,
TypeNameProviderPlugin.class,
SyntheticModelProviderPlugin.class
})
public class ModelsConfiguration {
@Bean
public TypeResolver typeResolver() {
return new TypeResolver();
}
}
和SpringfoxWebMvcConfiguration配置类行为相似,主要是:
- 扫描
springfox.documentation.schema进行实体bean的注入或者初始化工作 - 通过
EnablePluginRegistries插件开启注入相关插件的实体bean - 注入
TypeResolver实体bean到Spring容器中
SwaggerCommonConfiguration
Swagger的公共配置类
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {
"springfox.documentation.swagger.schema",
"springfox.documentation.swagger.readers",
"springfox.documentation.swagger.web"
})
public class SwaggerCommonConfiguration {
}
主要是进行backpage包的扫描,注入到Spring的容器中初始化相关的操作
思维导图
或许通过一张思维导图,我们能对本小结有一个初步的印象,对@EnableSwagger2注解的做作用有一个初步的了解
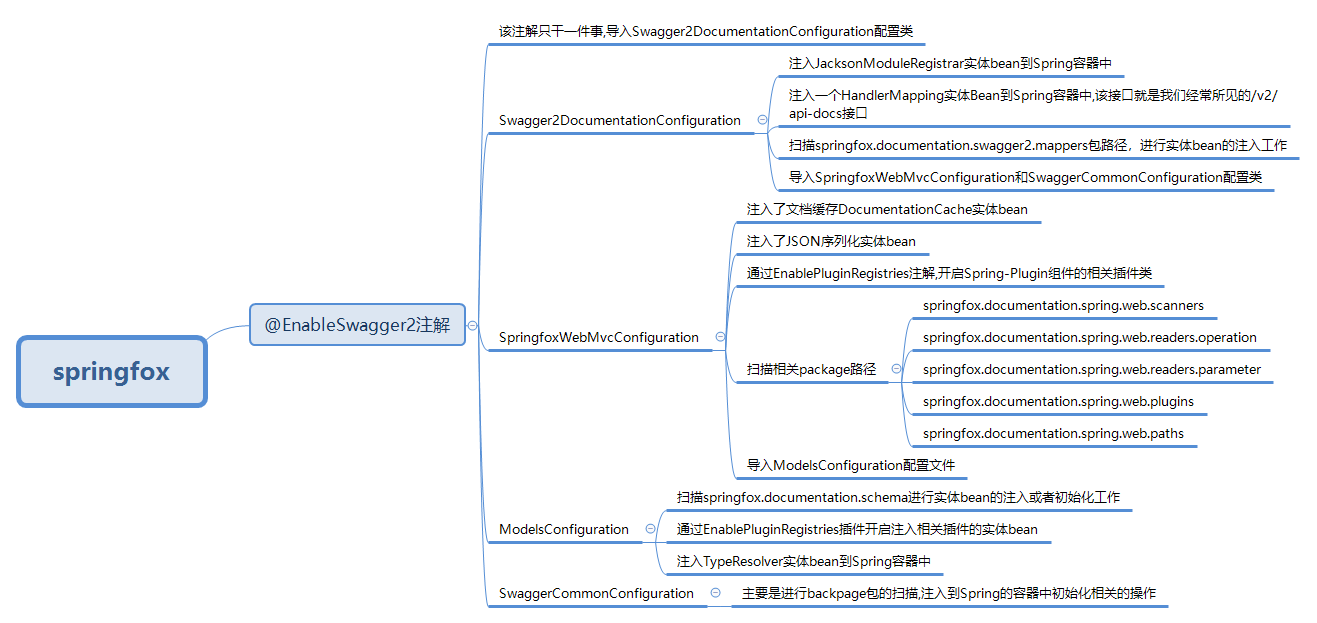
总结就是两点:
- 扫描package
- 注入bean
总结
整个springfox的初始化工作如果我们从上面来看,那绝对是灾难.心中肯定会有诸多疑问:
- 我们通过在外部创建Docket对象,提供诸如扫描接口包路径的方式进行文档分组,springfox何时初始化?
- 分组的接口代码在哪儿?
- 初始化的入口在哪儿?
这主要是因为Springfox使用Spring的@Component注解和ComponentScan扫描包导致的,让我们无从下手啊(累觉不爱)
带着这些疑问,我们继续往下看~~!