springfox 源码分析(十三) 自定义扩展实现接口的排序
很多时候,Swagger定义的标准并不能满足我们实际的需求,比如拿分组后的接口来说,有适合我们希望我们的接口能够排序,假如我们当前有一个注册的需求实现,那么他的接口可能是这样的:
1.获取验证码 -> 2.校验用户名是否有效 -> 3.注册验证 -> 4.登录
如果我们没有排序的情况下,上面的接口对于开发人员来说可能是杂乱无章的,对于初级的接口对接人员来说,排序更能让开发者把当前的需求清晰明了的用代码来实现掉,为此,接口文档的作用也能最大化.
那么,在swagger的标准中,那些允许我们自定义扩展,在Springfox中我们又如何来实现我们的自定义扩展呢?
Swagger标准
先来看Swagger定义的几个标准属性,可参考官方文档
| swagger | string | Required. Specifies the Swagger Specification version being used. It can be used by the Swagger UI and other clients to interpret the API listing. The value MUST be "2.0". |
|---|---|---|
| info | Info Object | Required. Provides metadata about the API. The metadata can be used by the clients if needed. |
| host | string | The host (name or ip) serving the API. This MUST be the host only and does not include the scheme nor sub-paths. It MAY include a port. If the host is not included, the host serving the documentation is to be used (including the port). The host does not support path templating. |
| basePath | string | The base path on which the API is served, which is relative to the host. If it is not included, the API is served directly under the host. The value MUST start with a leading slash (/). The basePath does not support path templating. |
| schemes | [string] | The transfer protocol of the API. Values MUST be from the list: "http", "https", "ws", "wss". If the schemes is not included, the default scheme to be used is the one used to access the Swagger definition itself. |
| consumes | [string] | A list of MIME types the APIs can consume. This is global to all APIs but can be overridden on specific API calls. Value MUST be as described under Mime Types. |
| produces | [string] | A list of MIME types the APIs can produce. This is global to all APIs but can be overridden on specific API calls. Value MUST be as described under Mime Types. |
| paths | Paths Object | Required. The available paths and operations for the API. |
| definitions | Definitions Object | An object to hold data types produced and consumed by operations. |
| parameters | Parameters Definitions Object | An object to hold parameters that can be used across operations. This property does not define global parameters for all operations. |
| responses | Responses Definitions Object | An object to hold responses that can be used across operations. This property does not define global responses for all operations. |
| securityDefinitions | Security Definitions Object | Security scheme definitions that can be used across the specification. |
| security | [Security Requirement Object] | A declaration of which security schemes are applied for the API as a whole. The list of values describes alternative security schemes that can be used (that is, there is a logical OR between the security requirements). Individual operations can override this definition. |
| tags | [Tag Object] | A list of tags used by the specification with additional metadata. The order of the tags can be used to reflect on their order by the parsing tools. Not all tags that are used by the Operation Objectmust be declared. The tags that are not declared may be organized randomly or based on the tools' logic. Each tag name in the list MUST be unique. |
| externalDocs | External Documentation Object | Additional external documentation. |
在上面定义的标准字段中,最后一个是扩展对象,我们在Java对象中io.swagger.models.Swagger中可以看到他的定义
public class Swagger {
protected String swagger = "2.0";
protected Info info;
protected String host;
protected String basePath;
protected List<Tag> tags;
protected List<Scheme> schemes;
protected List<String> consumes;
protected List<String> produces;
protected List<SecurityRequirement> security;
protected Map<String, Path> paths;
protected Map<String, SecuritySchemeDefinition> securityDefinitions;
protected Map<String, Model> definitions;
protected Map<String, Parameter> parameters;
protected Map<String, Response> responses;
protected ExternalDocs externalDocs;
//扩展属性
protected Map<String, Object> vendorExtensions;
//setter and getter
}
所以从上面的接口定义来看,我们最终可以来一一查看Swagger支持哪些对象进行自定义扩展属性
Swagger根对象扩展
在Swagger的根对象中,我们看到他是有vendorExtensions扩展属性的支持的,是一个散列的数据结构类型,这意味着我们可以在Swagger的根对象中添加多个扩展属性
扩展属性名称的规则必须是以x-来开头,所有的都是这个规则
| Field Pattern | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ^x- | Any | Allows extensions to the Swagger Schema. The field name MUST begin with x-, for example, x-internal-id. The value can be null, a primitive, an array or an object. See Vendor Extensions for further details. |
看到此处,以前在swagger-bootstrap-ui的1.8.5版本中添加的扩展属性都是不规范的,因为没有应用swagger的标准规则,在后期的版本中要重写该规则实现
所以,我们在Swagger根路径扩展的规则最终生成的JSON格式可能是这样:
{
"swagger": "2.0",
"info": {
"description": "<div style='font-size:14px;color:red;'>swagger-bootstrap-ui-demo RESTful APIs</div>",
"version": "1.0",
"title": "swagger-bootstrap-ui很棒~~~!!!",
"termsOfService": "http://www.group.com/",
"contact": {
"name": "group@qq.com"
}
},
"host": "127.0.0.1:8999",
"basePath": "/",
"tags": [
{
"name": "1.8.2版本",
"description": "Api 182 Controller"
}
],
"paths": {
"/2/api/new187/postRequest": {
"post": {
"tags": [
"api-1871-controller"
],
"summary": "版本2-post请求参数Hidden属性是否生效",
"operationId": "postRequestUsingPOST_1",
"consumes": [
"application/json"
],
"produces": [
"*/*"
],
"parameters": [
{
"in": "body",
"name": "model187",
"description": "model187",
"required": true,
"schema": {
"originalRef": "Model187",
"$ref": "#/definitions/Model187"
}
}
],
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "OK",
"schema": {
"originalRef": "Rest«Model187»",
"$ref": "#/definitions/Rest«Model187»"
}
},
"201": {
"description": "Created"
},
"401": {
"description": "Unauthorized"
},
"403": {
"description": "Forbidden"
},
"404": {
"description": "Not Found"
}
},
"security": [
{
"BearerToken": [
"global"
]
},
{
"BearerToken1": [
"global"
]
}
],
"deprecated": false
}
}
},
"securityDefinitions": {
"BearerToken": {
"type": "apiKey",
"name": "Authorization",
"in": "header"
}
},
"definitions": {
"AInfoVo": {
"type": "object",
"required": [
"aId",
"bList"
],
"properties": {
"aId": {
"type": "string",
"description": "A记录主键"
},
"bList": {
"type": "object",
"description": "B信息Map, key为BInfoVo的主键pkId",
"additionalProperties": {
"originalRef": "BInfoVo",
"$ref": "#/definitions/BInfoVo"
}
}
},
"title": "AInfoVo",
"description": "A信息"
},
"ActInteger": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"doub1": {
"type": "number",
"format": "double",
"description": "double类型属性"
},
"float1": {
"type": "number",
"format": "float",
"description": "float类型属性"
},
"name": {
"type": "string"
},
"number": {
"type": "integer",
"format": "int64",
"description": "Long类型"
},
"price": {
"type": "number",
"description": "BigDecimal类型属性"
},
"sort": {
"type": "integer",
"format": "int32",
"description": "int类型"
}
},
"title": "ActInteger"
},
"Actor": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"address": {
"type": "string"
},
"deepOne": {
"originalRef": "DeepOne",
"$ref": "#/definitions/DeepOne"
},
"recipt": {
"originalRef": "Recipt",
"$ref": "#/definitions/Recipt"
},
"sort": {
"type": "integer",
"format": "int32"
}
},
"title": "Actor"
}
},
"x-description":"Swagger扩展属性之一Description"
}
x-description属性就是我们扩展的标准的扩展属性,我们在Java代码中也可以这么来实现:
Swagger swagger = mapper.mapDocumentation(documentation);
swagger.setVendorExtension("x-description","Swagger扩展属性之一Description");
path接口扩展
同上面的规则,path中定义的属性,我们同样可以扩展我们的规则,此时我们的需求,根据接口来排序就可以通过path增加扩展属性来实现,比如我们给path添加一个扩展属性x-order
path的JSON结构就可能如下:
"/2/api/new187/postRequest": {
"post": {
"tags": [
"api-1871-controller"
],
"summary": "版本2-post请求参数Hidden属性是否生效",
"operationId": "postRequestUsingPOST_1",
"consumes": [
"application/json"
],
"produces": [
"*/*"
],
"parameters": [
{
"in": "body",
"name": "model187",
"description": "model187",
"required": true,
"schema": {
"originalRef": "Model187",
"$ref": "#/definitions/Model187"
}
}
],
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "OK",
"schema": {
"originalRef": "Rest«Model187»",
"$ref": "#/definitions/Rest«Model187»"
}
},
"201": {
"description": "Created"
},
"401": {
"description": "Unauthorized"
},
"403": {
"description": "Forbidden"
},
"404": {
"description": "Not Found"
}
},
"security": [
{
"BearerToken": [
"global"
]
},
{
"BearerToken1": [
"global"
]
}
],
"deprecated": false,
"x-order":"1"
}
}
more
swagger在Open API的规范文档中声明的是任意对象都可以有对象扩展,只要符合扩展规则即可(即扩展属性名称以x-开头)
Springfox实现
我们知道了扩展规则的定义,那么在Springfox中我们如何自定义实现呢?
在前面的文章中,我们介绍了springfox使用了Spring Plugin系统来增强整个框架的可扩展性,我想此时的你应该能明白了,如果要扩展path接口的属性,那么,其实我们只需要找到Springfox提供的Plugin接口,然后增加一个Plugin的接口实现,把我们的扩展属性增加进去即可
接下来,我们实现上面path接口的自定义x-order的属性扩展实现.
我们先来看Springfox将自己的Documentation对象转换为Swagger标准对象的代码
@Override
public Swagger mapDocumentation(Documentation from) {
if ( from == null ) {
return null;
}
Swagger swagger = new Swagger();
swagger.setVendorExtensions( vendorExtensionsMapper.mapExtensions( from.getVendorExtensions() ) );
swagger.setSchemes( mapSchemes( from.getSchemes() ) );
//path转换
swagger.setPaths( mapApiListings( from.getApiListings() ) );
swagger.setHost( from.getHost() );
swagger.setDefinitions( modelMapper.modelsFromApiListings( from.getApiListings() ) );
swagger.setSecurityDefinitions( securityMapper.toSecuritySchemeDefinitions( from.getResourceListing() ) );
ApiInfo info = fromResourceListingInfo( from );
if ( info != null ) {
swagger.setInfo( mapApiInfo( info ) );
}
swagger.setBasePath( from.getBasePath() );
swagger.setTags( tagSetToTagList( from.getTags() ) );
List<String> list2 = from.getConsumes();
if ( list2 != null ) {
swagger.setConsumes( new ArrayList<String>( list2 ) );
}
else {
swagger.setConsumes( null );
}
List<String> list3 = from.getProduces();
if ( list3 != null ) {
swagger.setProduces( new ArrayList<String>( list3 ) );
}
else {
swagger.setProduces( null );
}
return swagger;
}
既然我们的目标是path,那么来看mapApiListings方法
protected Map<String, Path> mapApiListings(Multimap<String, ApiListing> apiListings) {
Map<String, Path> paths = newTreeMap();
for (ApiListing each : apiListings.values()) {
for (ApiDescription api : each.getApis()) {
paths.put(api.getPath(), mapOperations(api, Optional.fromNullable(paths.get(api.getPath()))));
}
}
return paths;
}
程序的逻辑是:
- 声明一个map数组,key是接口路径,value是path对象
- 遍历springfox中的ApiListing集合对象(类似于controller)
- 遍历ApiDescription结合对象(类似于接口method)
- 最终拿到apiDescription的接口地址,将operation对象转换为path
继续来看mapOperations方法
private Path mapOperations(ApiDescription api, Optional<Path> existingPath) {
Path path = existingPath.or(new Path());
for (springfox.documentation.service.Operation each : nullToEmptyList(api.getOperations())) {
Operation operation = mapOperation(each);
path.set(each.getMethod().toString().toLowerCase(), operation);
}
return path;
}
循环遍历所有的Operation,此处为什么有循环,因为我们同一个接口允许存在不同的请求方式(GET|POST|PUT|DELETE...),但是请求体可以相同
@Override
protected io.swagger.models.Operation mapOperation(Operation from) {
if ( from == null ) {
return null;
}
io.swagger.models.Operation operation = new io.swagger.models.Operation();
operation.setSecurity( mapAuthorizations( from.getSecurityReferences() ) );
operation.setVendorExtensions( vendorExtensionsMapper.mapExtensions( from.getVendorExtensions() ) );
看到mapOperation方法时,我们终于看到了setVendorExtensions的操作,即赋值扩展属性
那么来看扩展属性是如何来实现的
@Mapper
public class VendorExtensionsMapper {
public Map<String, Object> mapExtensions(List<VendorExtension> from) {
Map<String, Object> extensions = newTreeMap();
Iterable<ListVendorExtension> listExtensions = from(from)
.filter(ListVendorExtension.class);
for (ListVendorExtension each : listExtensions) {
extensions.put(each.getName(), each.getValue());
}
Iterable<Map<String, Object>> objectExtensions = from(from)
.filter(ObjectVendorExtension.class)
.transform(toExtensionMap());
for (Map<String, Object> each : objectExtensions) {
extensions.putAll(each);
}
Iterable<StringVendorExtension> propertyExtensions = from(from)
.filter(StringVendorExtension.class);
for (StringVendorExtension each : propertyExtensions) {
extensions.put(each.getName(), each.getValue());
}
return extensions;
}
通过VendorExtensionsMapper中的扩展属性方法,我们看到,springfox目前做了限制,因为VendorExtension是接口,我们可以有我们自己的定义实现,但是springfox最终会对扩展接口进行filter过滤,从代码中我们看到,springfox目前只允许三种扩展实现
分别是:
- ListVendorExtension:列表的形式,该对象支持泛型,最终形式:"x-field":[{field:value}]
- ObjectVendorExtension:对象的扩展形式,最终的扩展形式是:"x-field":[{field:value}]
- StringVendorExtension:string类型的扩展实现,最终的扩展形式是"x-field":"value"
既然springfox给我们提供了默认的三种扩展实现,那么针对上面的我们需要扩展path的扩展属性,我们使用StringVendorExtension:string这种类型即可
针对path的operation操作,我们在前面也介绍过,springfox最终使用的是OperationBuilderPlugin接口
那么我们只需要写一个OperationBuilderPluginPlugin接口的实现即可
@Component
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE+100)
public class OperationPositionBulderPlugin implements OperationBuilderPlugin {
@Override
public void apply(OperationContext context) {
context.operationBuilder().extensions(Lists.newArrayList(new StringVendorExtension("x-order","1")));
}
@Override
public boolean supports(DocumentationType delimiter) {
return true;
}
}
目前假设我们给所有的接口都赋予扩展属性x-order,默认值为"1"
此时,我们来看/v2/api-docs接口响应的JSON示例
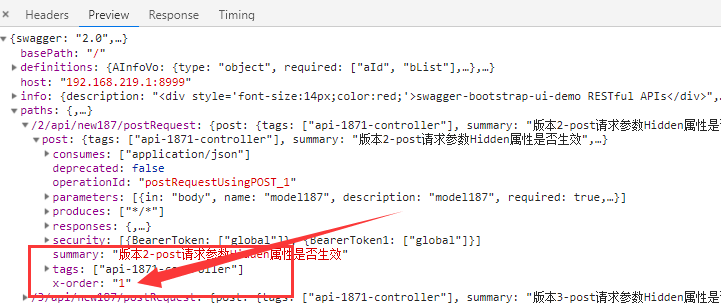
上图中,我们其实可以看到我们的自定义扩展属性实现了
然后我们在结合我们自定义的swagger-bootstrap-ui前端UI渲染程序,把order字段作为path接口的排序字段,在页面进行排序显示,这样我们就实现了我们的接口自定义排序规则了
有可能细心的朋友会问,我们给的order值都是1,如果给与开发者在代码中给接口自定义的值呢
此时,有两种方式
- 基于swagger-bootstrap-ui提供的注解
@ApiOperationSort进行获取 - 基于swagger的默认注解
@ApiOperation中的postion属性进行二次利用
此时,我们的接口代码可能会如下:
@PostMapping("/createOr33der")
@ApiOperation(value = "创建订单",position = 2)
public Rest<Order> createOrdetr(@RequestBody Order order,HttpSession httpSession){
Rest<Order> r=new Rest<>();
r.setData(order);
return r;
}
@PostMapping("/createOrder")
@ApiOperationSort(3)
@ApiOperation(value = "hash测试",nickname = "test")
public Rest<Order> createOrder(@RequestBody Order order){
Rest<Order> r=new Rest<>();
r.setData(order);
return r;
}
两种方式,取第一种即可
这时,我们更改一下上面我们的Plugin接口实现
@Override
public void apply(OperationContext context) {
int position=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
//首先查找ApiOperation注解
Optional<ApiOperation> api=context.findAnnotation(ApiOperation.class);
if (api.isPresent()){
//判断postion是否有值
int posit=api.get().position();
if (posit!=0){
position=posit;
}else{
Optional<ApiOperationSort> apiOperationSortOptional=context.findAnnotation(ApiOperationSort.class);
if (apiOperationSortOptional.isPresent()){
position=apiOperationSortOptional.get().value();
}
}
}else{
Optional<ApiOperationSort> apiOperationSortOptional=context.findAnnotation(ApiOperationSort.class);
if (apiOperationSortOptional.isPresent()){
position=apiOperationSortOptional.get().value();
}
}
context.operationBuilder().extensions(Lists.newArrayList(new StringVendorExtension("x-order",String.valueOf(position))));
}
此时,我们再来看JSON效果
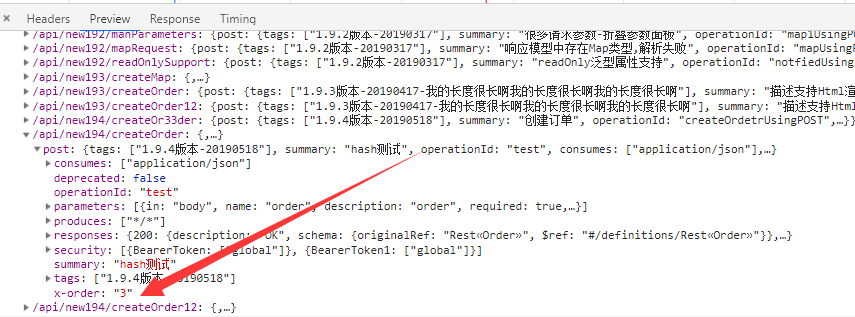
此时,我们看到,我们的自定义属性已经出现了,而且是根据开发者自定义的实现,此时我们的目的也达到了.